PhotoElectroCatalysis for Energy and the Environment
Keywords
- bimetallic
- catalysis
- cavity microelectrode
- CO2
- remediation
- electrochemistry
- hematite
- MACE nanostructuring
- semiconductor
- silicon
- photoelectrochemistry
- photovoltaics
- texturization
- urea
Group leader
Members
Non permanent researchers
Scientific activities
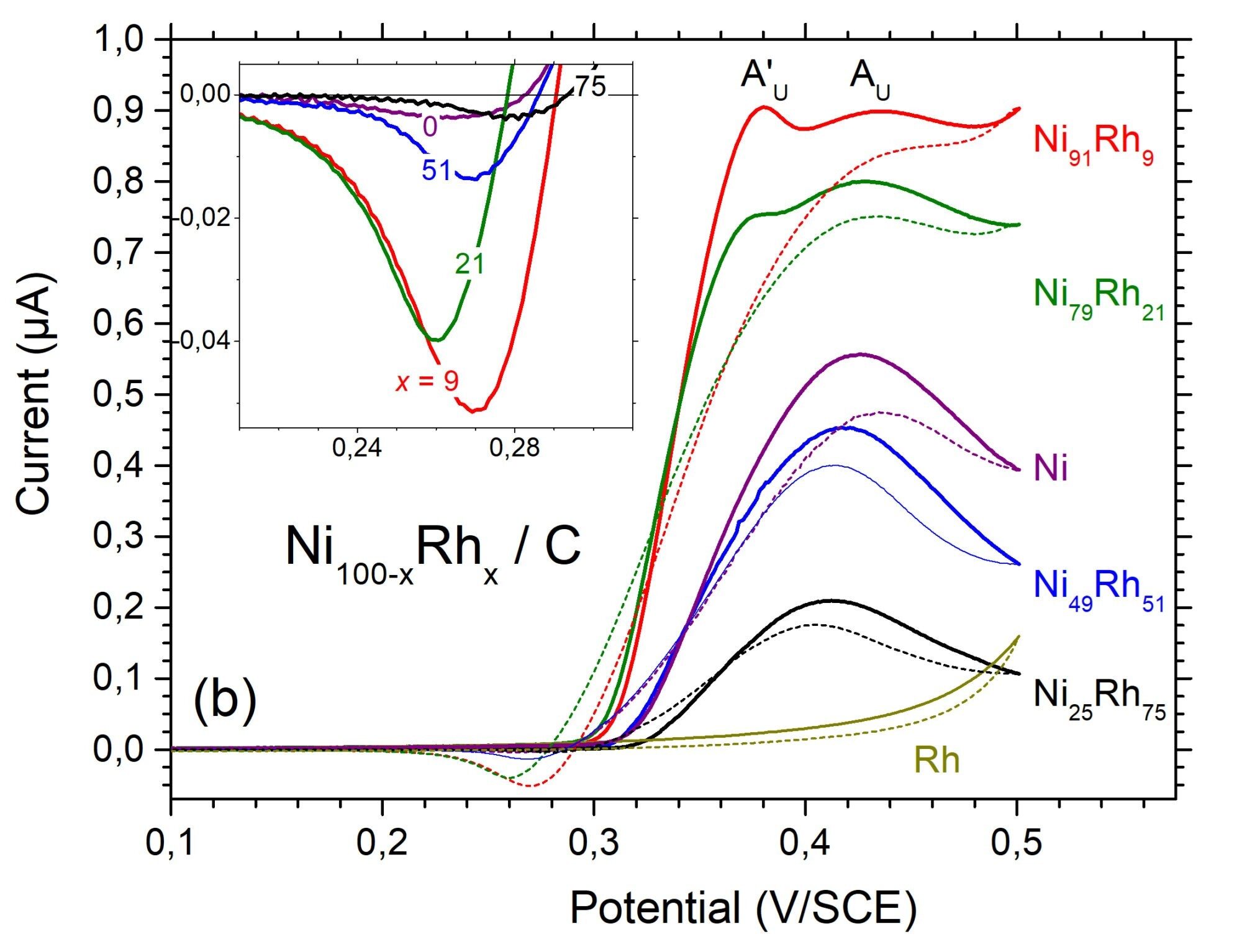
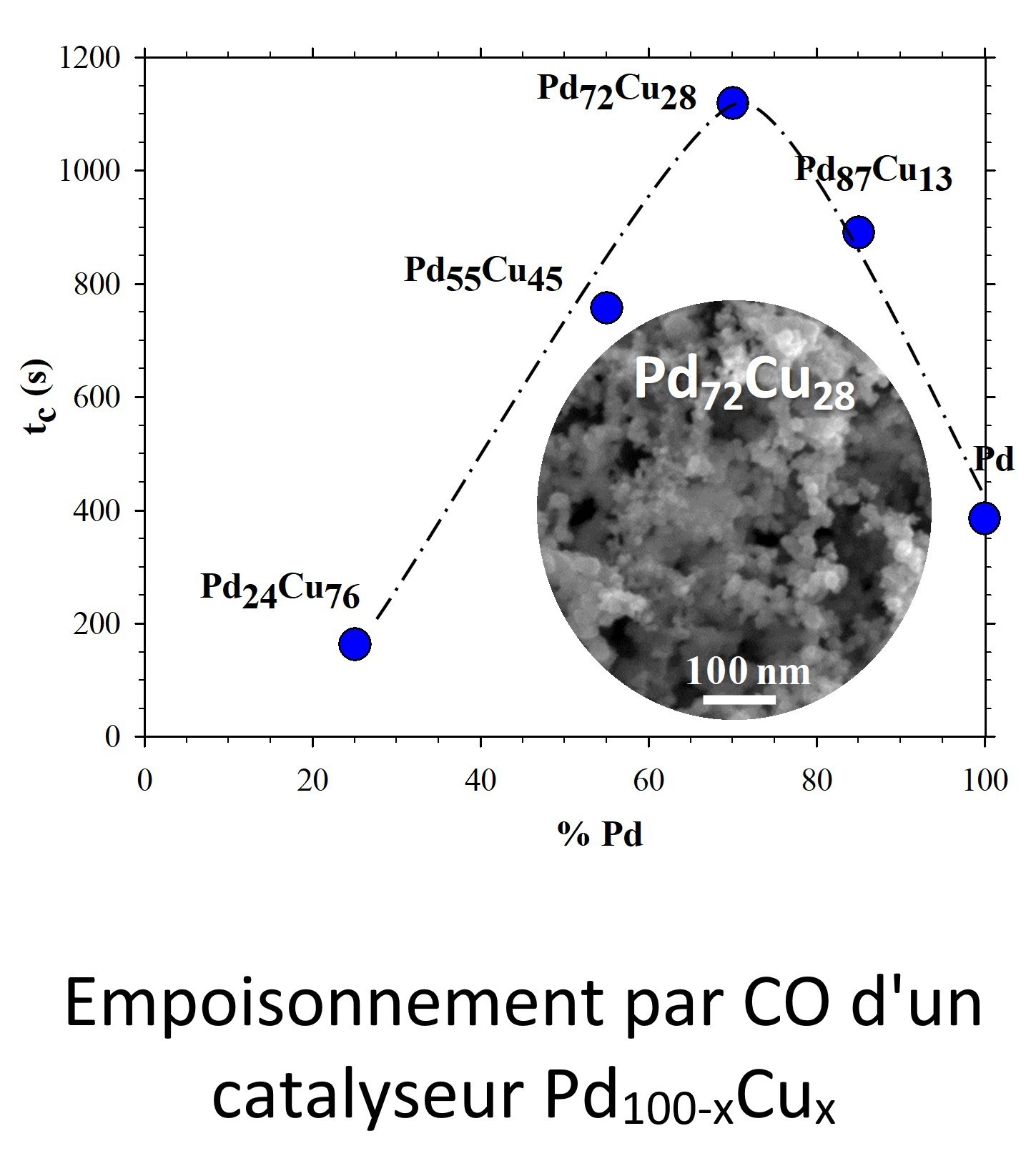
ICMPE’s Group of PhotoElectroCatalysis for Energy and the Environment (PECEE) develops processes for the elimination and valorization of pollutants such as urea (e.g. in collected urine), nitrates (e.g. in industrial or agricultural liquid effluents), or CO2(industrial gaseous effluents). In this context, it elaborates electrode materials composed of photoactive semiconductors on the one hand and supported bimetallic catalysts on the other hand, whose composition and nanostructuring are optimized.
- Electrochemistry is the main investigation tool, in particular, to study the catalytic properties of bimetallics according to their composition and to analyze the photoelectrochemical response of composite electrodes according to the nature of the semiconductor (e.g. Si, Fe2O3), the electrolyte, and the type of pollutants.
- PECEE is also working on the development (experimental and theoretical) of a specific electrode dedicated to the characterization of powders, the Cavity MicroElectrode (CME), which allows improving the quality of the electrochemical signals and the use of minute quantities of materials (10-8 g).
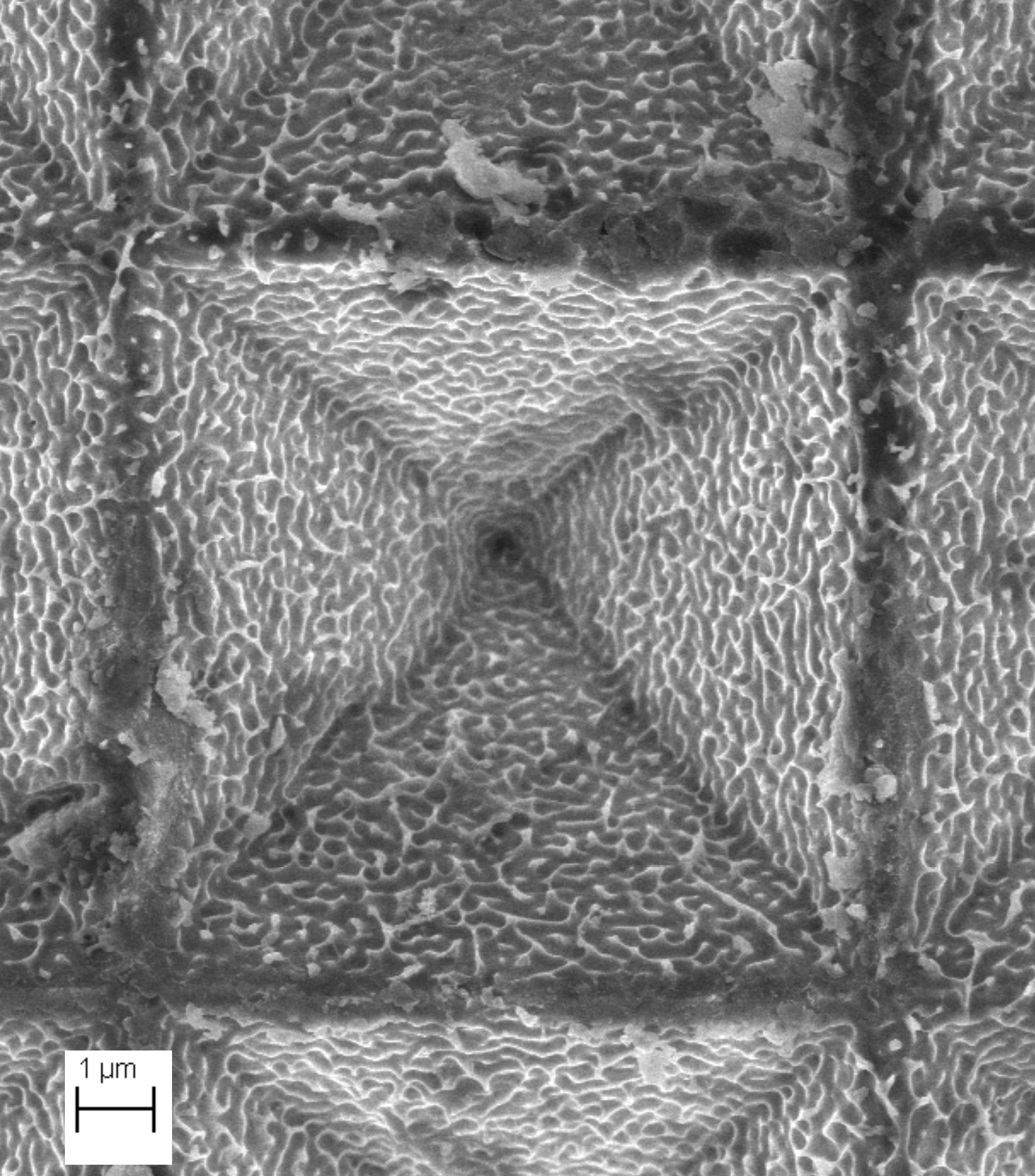
- Finally, the group studies the surface structuring of silicon by chemical methods based on noble metal-assisted chemical etching in HF medium (MACE) for optoelectronic devices (e.g. 3D printing of complex structures without lithography, texturization of Si solar cells, elaboration of Si nanowires).
Illustrations

(a) Preparation of biochar from olive pits, (b) olive pit powder, (c) after impregnation with Cu and Ni nitrates, (d) olive pit biochar, (e) CuNi-decorated biochar from direct pyrolysis of (c), (f) suspension of (e) and its magnetic collection (right).